
| Parasite | Benedenia epinepheli |
|---|---|
| Taxonomy | Plathyhelminthes, Monogenea, Monopisthocotylea |
| Hosts | Marine fishes including Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes), convict grouper (Epinephelus septemfasciatus), Hong Kong grouper (E. akaara), Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) and viviparous scorpionfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus). |
| Infection site | Skin, fin |
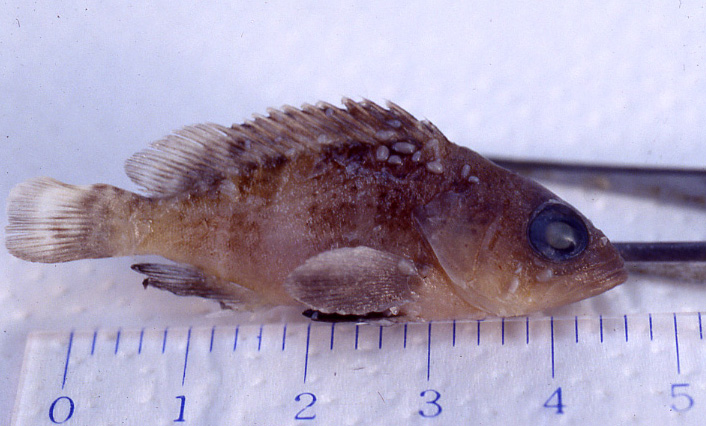
| Clinical sign | Transparent parasites attach on the skin and the fin (Fig. 1). Skin injuries are observed in heavily infected fish. |
| Parasitology | Benedenia epinepheli is flat, oval and small (body length 2-3 mm) compared with other skin flukes. The parasite attaches to the host by a haptor with 2 pairs of anchors at the posterior end and a pair of suckers at the anterior end. The hermaphroditic adult produces eggs with filamentous threads. This parasite has very wide host range like Neobenedenia girellae. A total of 25 fish species (13 families), including wild, cultured and aquarium fishes, serve as hosts for this parasite (Ogawa et al., 1995). |
| Pathology | Secondary infection of microorganisms may occur at the skin lesion. |
| Health hazard | Since this parasite is not infectious to human, it is harmless in food hygiene. |
| Diagnosis | The parasite can be identified by morphological observation in a flattened preparation. Benedenia epinepheli can be distinguished from Neobenedenia girellae: N. girellae is larger (body length 3-8 mm). Benedenia epinepheli has a prominent flap-like structure slightly left of common genital aperture, which is uncommon in other Benedenia species (Ogawa, 2004). |
| Other information |
Since 1989, the parasite has been found from cultured Japanese marine fishes, but the origin is unknown. Freshwater-bath may be effective for control of the parasite. |
| References | Ogawa, K., M. G.
Bondad-Reantaso and H. Wakabayashi (1995): Redescription of Benedenia epinepheli (Yamaguti, 1937) Meserve, 1938 (Monogenea: Capsalidae) from cultured and
aquarium marine fishes of Japan. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 52 (Suppl. 1), 62-70. Ogawa, K. (2004): Monogenean diseases. Infectious and parasitic diseases of fish and shellfish. (ed. by Wakabayashi, H. and K. Muroga), Koseisha Koseikaku, pp.353-379. (In Japanese) |

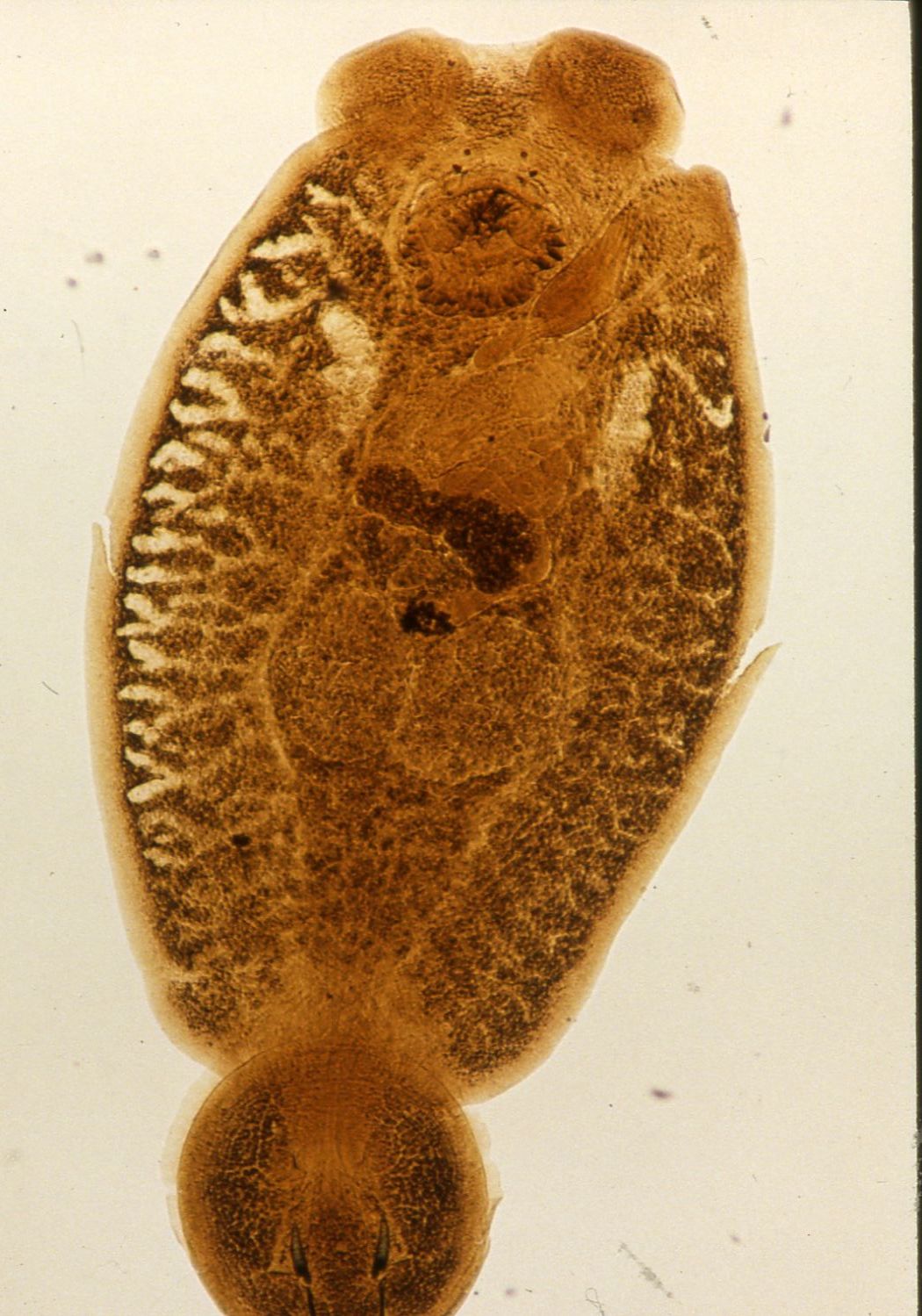
Fig. 1. A fry of Hong Kong grouper parasitized by B. epinepheli.
Fig. 2. Adult of B. epinepheli from Japanese flounder.
(Photos by K. Ogawa)